The Moon will pass through the Earth's shadow between 20:08 and 22:53 PDT, creating a penumbral lunar eclipse. The eclipse will be visible any location where the Moon is above the horizon at the time, including from Antarctica, the Americas and Africa.
It will be visible from South El Monte in the south-eastern sky. The Moon will lie 14° above the horizon at the moment of greatest eclipse.
Maximum eclipse will occur at 21:31 (all times given in South El Monte time).
The simulation to the right shows Moon's path relative to the Earth's shadow. The outer grey circle is the Earth's penumbra, within which the Earth blocks part of the Sun's light, making the Moon appear less bright than usual, but not completely dark. The inner black circle is the umbra, within which the Earth entirely blocks the Sun's light, and where the Moon's disk would appear entirely unilluminated.
By default the eclipse is drawn with the local vertical in South El Monte uppermost (Zenith up), so that it is orientated as you would see it looking up at the Moon. The compass shows the direction of celestial north relative to the local vertical. Alternatively, you can orientate the sky with celestial north orientated uppermost, by selecting the option North up.
Selecting the option Diagram of Moon's path produces a static display of the Moon's path over the duration of the eclipse.
The lower panel shows the Moon's position in the sky relative to the horizon, as seen from South El Monte.
A penumbral eclipse
Like other lunar eclipses, penumbral eclipses occur whenever the Earth passes between the Moon and Sun, such that it obscures the Sun's light and casts a shadow onto the Moon's surface. But unlike other kinds of eclipses, they are extremely subtle events to observe.
In a penumbral eclipse the Moon passes through an outer region of the Earth's shadow called the penumbra. This is the outer part of the Earth's shadow, in which the Earth appears to cover part of the Sun's disk, but not all of it (see diagram below). As a result, the Moon's brightness will be reduced, as it is less strongly illuminated by the Sun, but the whole of the Moon's disk will remain illuminated to some degree.
The effect is only perceptible to those with very astute vision, or in carefully controlled photographs.
Moreover, on this occasion no more than 35% of the Moon's face will pass within the Earth's penumbra, even at the moment of greatest eclipse, making it especially difficult to notice any reduction in the Moon's brightness.

Timing
The table below lists the times when each part of the eclipse will begin and end.
| Local time |
UTC | |
| 20:08 | 03:08 | Moon begins to enter the Earth's penumbra |
| 21:31 | 04:31 | Greatest eclipse |
| 22:53 | 05:53 | Moon leaves the Earth's penumbra |
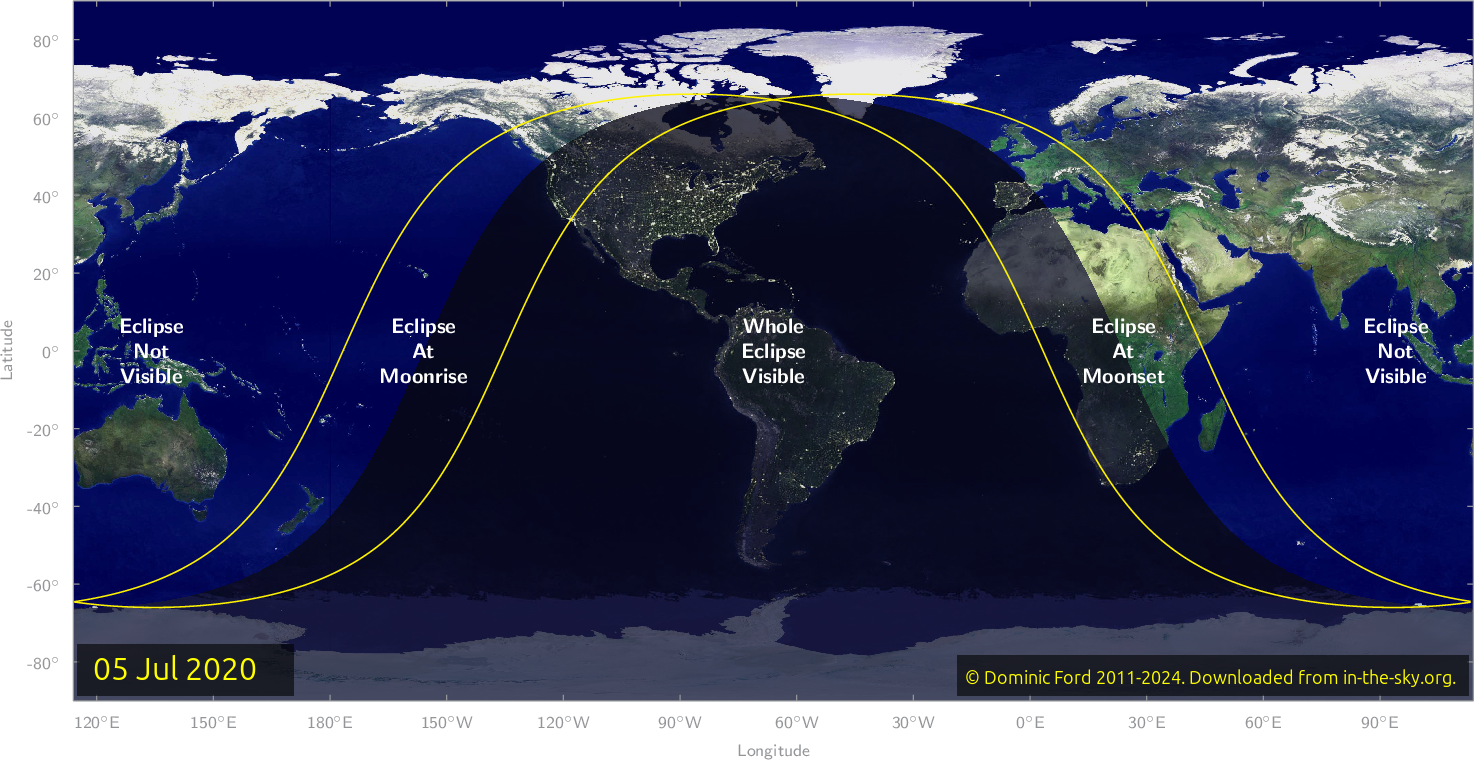
Visibility of the eclipse
Eclipses of the Moon are visible anywhere where the Moon is above the horizon at the time. Since the geometry of lunar eclipses requires that the Moon is directly opposite the Sun in the sky, the Moon can be seen above the horizon anywhere where the Sun is beneath the horizon.
The map below shows where the eclipse of July 4 will be visible.
The eclipse geometry
Lunar eclipses occur when the Sun, Earth and Moon are aligned in a straight line, so that the Earth passes between the Sun and Moon and casts a shadow onto the latter's surface.
Each time the Moon orbits the Earth, it passes almost opposite to the Sun in the sky as it reaches Full Moon. If the Moon orbited the Earth in exactly the same plane that the Earth orbits the Sun, the Earth would pass between the Sun and Moon and create a lunar eclipse at Full Moon every month.
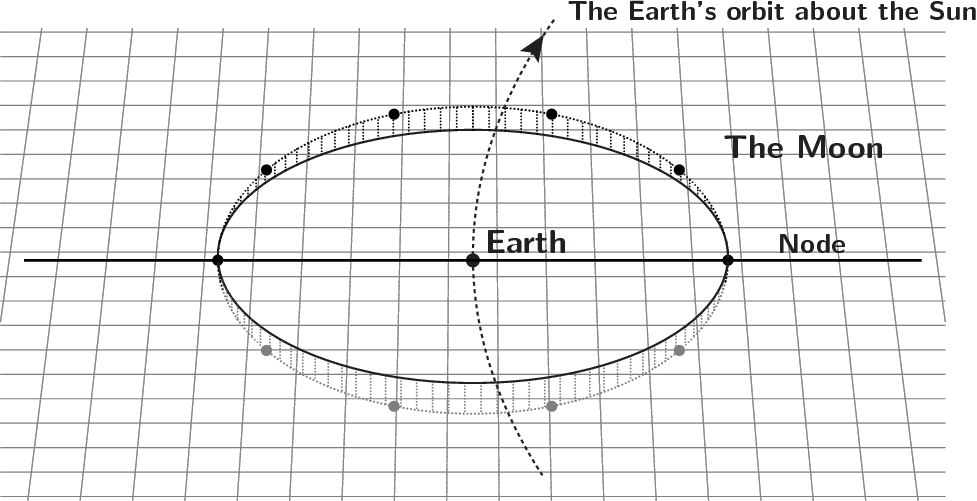

In fact, the Moon's orbit is tipped up at an angle of 5° relative to the Earth's orbit around the Sun. This means that the alignment of the Sun—Earth—Moon line at Full Moon usually isn't exact. As a result, an observer on the Moon would see the Earth pass a few degrees to the side of the Sun.
In the diagram to the right, the grid represents the plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. As it circles the Earth, the Moon passes through this Earth–Sun plane twice each month, at the points on the left and right labelled as nodes. A lunar eclipse happens only when one of these node crossings happens to coincide with Full Moon. This happens roughly once every six months, usually two weeks before or after a solar eclipse.
Further information
This eclipse is a member of Saros series 149. The position of the Moon at the moment of greatest eclipse is as follows:
| Object | Right Ascension | Declination | Constellation | Angular Size |
| The Moon | 18h58m | 24°04'S | Sagittarius | 31'30" |
The coordinates above are given in J2000.0.
Next/previous eclipses
| « Previous | Next » | |||
| Visible from the Contiguous United States | Worldwide | Worldwide | Visible from the Contiguous United States | |
| 11 Feb 2017 | 05 Jun 2020 | Penumbral Lunar Eclipses | 30 Nov 2020 | 30 Nov 2020 |
| 21 Jan 2019 | 05 Jun 2020 | Lunar Eclipses | 30 Nov 2020 | 30 Nov 2020 |
| 21 Jan 2019 | 21 Jun 2020 | Eclipses | 30 Nov 2020 | 30 Nov 2020 |
The sky on 4 Jul 2020
| The sky on 4 July 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
99% 14 days old |
All times shown in PDT.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source
|
[1] – |
The lunar eclipse predictions presented on this website were computed using EphemerisCompute. This is an open-source tool which traces the positions of the Sun, Earth and Moon over the course of each eclipse and traces the path of the Moon through the Earth's shadow. It was written by the author and freely available for download from GitHub. It takes the positions of each body from the JPL DE430 planetary ephemeris. |
|
[2] – |
Espanak, F., & Meeus, J., Five Millennium Canon of Solar Eclipses: -1999 to +3000, NASA Technical Publication TP-2006-214141 (2006) |
|
[3] – |
The list of countries from which the eclipse is visible was computed on the basis of shape files available from DIVA-GIS. |
License
You may embed the map above in your own website. It is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license, which allows you to copy and/or modify it, so long as you credit In-The-Sky.org.
You can download it from:
https://in-the-sky.org/news/eclipses/lunar_20200705.png
Related news
| 28 Jun 2020 | – Moon at First Quarter |
| 04 Jul 2020 | – Full Moon |
| 12 Jul 2020 | – Moon at Last Quarter |
| 20 Jul 2020 | – New Moon |
Image credit
None available.
