Asteroid 3 Juno will be well placed, lying in the constellation Leo, well above the horizon for much of the night.
Regardless of your location on the Earth, 3 Juno will reach its highest point in the sky around midnight local time.
From South El Monte, it will be visible between 19:31 and 04:21. It will become accessible at around 19:31, when it rises to an altitude of 21° above your eastern horizon. It will reach its highest point in the sky at 23:56, 60° above your southern horizon. It will become inaccessible at around 04:21 when it sinks below 21° above your western horizon.
The geometry of the alignment
This optimal positioning occurs when it makes its closest approach to the point in the sky directly opposite to the Sun – an event termed opposition. Since the Sun reaches its greatest distance below the horizon at midnight, the point opposite to it is highest in the sky at the same time.
At around the same time that 3 Juno passes opposition, it also makes its closest approach to the Earth – termed its perigee – making it appear at its brightest in the night sky. This happens because when 3 Juno lies opposite to the Sun in the night sky, the solar system is lined up so that 3 Juno, the Earth and the Sun lie in a straight line with the Earth in the middle, on the same side of the Sun as 3 Juno.
On this occasion, 3 Juno will pass within 1.687 AU of us, reaching a peak brightness of magnitude 8.6. Nonetheless, even at its brightest, 3 Juno is a faint object beyond the reach of the naked eye; binoculars or a telescope of moderate aperture are needed.
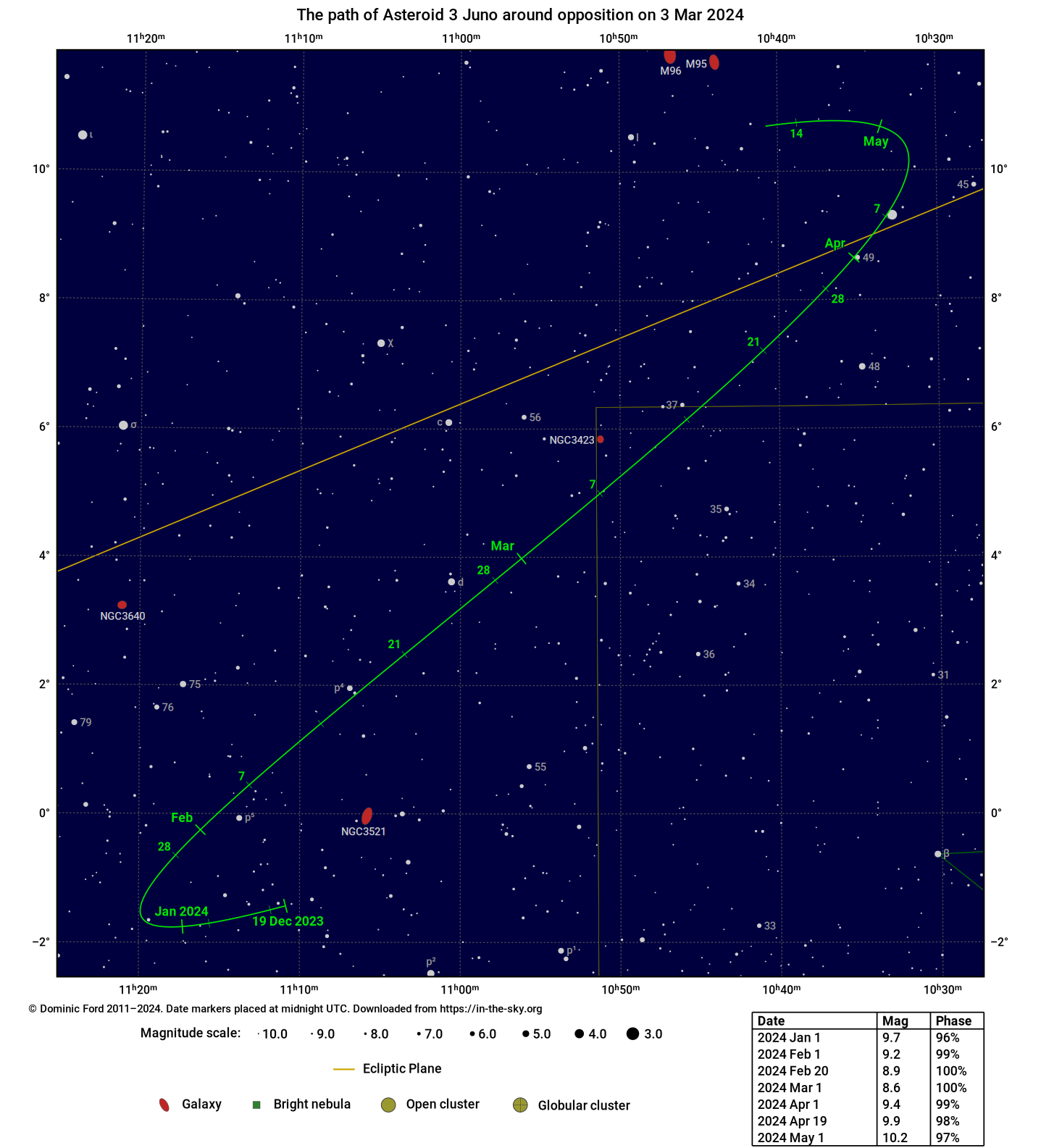
Finding 3 Juno
The chart below indicates the path of 3 Juno across the sky around the time of opposition.
It was produced using StarCharter and is available for download, either on dark background, in PNG, PDF or SVG formats, or on a light background, in PNG, PDF or SVG formats.
The position of 3 Juno at the moment of opposition will be as follows:
The coordinates above are given in J2000.0.
The sky on 3 Mar 2024
| The sky on 3 March 2024 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
41% 23 days old |
All times shown in PST.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source
The circumstances of this event were computed from orbital elements made available by Ted Bowell of the Lowell Observatory. The conversion to geocentric coordinates was performed using the position of the Earth recorded in the DE430 ephemeris published by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
The star chart above shows the positions and magnitudes of stars as they appear in the Tycho catalogue. The data was reduced by the author and plotted using PyXPlot. A gnomonic projection of the sky has been used; celestial coordinates are indicated in the J2000.0 coordinate system.
Image credit
© European Southern Observatory 2021. Credit: ESO/M. Kornmesser/Vernazza et al./MISTRAL algorithm (ONERA/CNRS).