Mars will enter retrograde motion, halting its usual eastward movement through the constellations, and turning to move westwards instead. This reversal of direction is a phenomenon that all the solar system's outer planets periodically undergo, a few months before they reach opposition.
The retrograde motion is caused by the Earth's own motion around the Sun. As the Earth circles the Sun, our perspective changes, and this causes the apparent positions of objects to move from side-to-side in the sky with a one-year period. This nodding motion is super-imposed on the planet's long-term eastward motion through the constellations.
The diagram below illustrates this. The grey dashed arrow shows the Earth's sight-line to the planet, and the diagram on the right shows the planet's apparently movement across the sky as seen from the Earth:
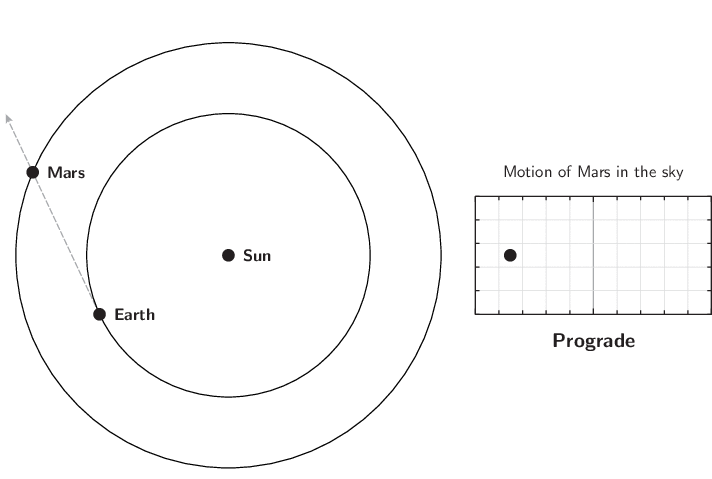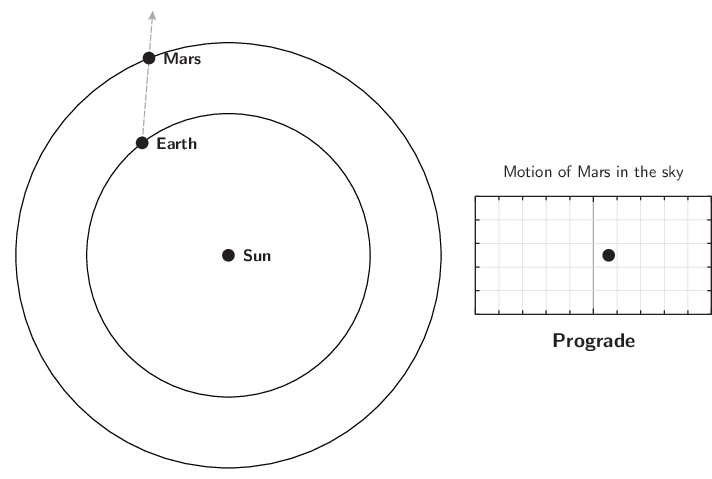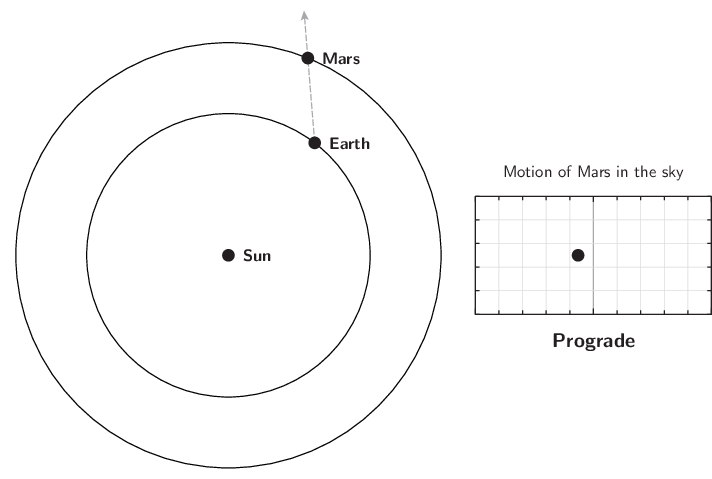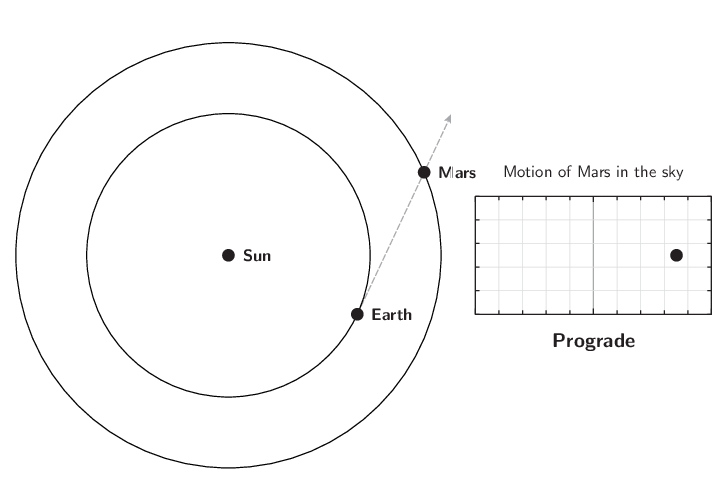
The retrograde motion of Mars.
Not drawn to scale.
The panels below show the month-by-month change in Mars' apparent size in coming weeks:
Observing Mars
Mars enters retrograde motion as its 2050 apparition gets underway, although it has already been visible for some weeks in the pre-dawn sky.
As retrograde motion starts, it will be visible in the morning sky, becoming accessible around 22:57, when it reaches an altitude of 7° above your south-eastern horizon. It will then reach its highest point in the sky at 03:23, 37° above your southern horizon. It will be lost to dawn twilight around 05:29, 29° above your south-western horizon.
Over the following weeks, Mars will reach its highest point in the sky four minutes earlier each night, gradually becoming visible in the evening sky, as well as the pre-dawn sky, as it approaches opposition.
The table below lists Mars' angular size and brightness at two-week intervals throughout its apparition:
| Date | Right ascension | Declination | Angular size | Magnitude |
| 05 Jun 2050 | 21h22m10s | 18°36'S | 14.2” | -1.0 |
| 19 Jun 2050 | 21h42m40s | 17°51'S | 16.4” | -1.4 |
| 03 Jul 2050 | 21h56m10s | 17°42'S | 19.0” | -1.8 |
| 17 Jul 2050 | 22h01m00s | 18°18'S | 21.7” | -2.3 |
| 31 Jul 2050 | 21h55m50s | 19°34'S | 24.0” | -2.6 |
| 14 Aug 2050 | 21h43m00s | 20°58'S | 25.0” | -2.9 |
| 28 Aug 2050 | 21h28m50s | 21°44'S | 24.3” | -2.7 |
| 11 Sep 2050 | 21h21m10s | 21°28'S | 22.2” | -2.3 |
| 25 Sep 2050 | 21h23m30s | 20°14'S | 19.6” | -1.9 |
| 09 Oct 2050 | 21h35m30s | 18°15'S | 17.0” | -1.5 |
| 23 Oct 2050 | 21h54m40s | 15°41'S | 14.7” | -1.1 |
As it begins retrograde motion, its celestial coordinates will be:
| Object | Right Ascension | Declination | Constellation | Magnitude | Angular Size |
| Mars | 22h01m00s | 18°09'S | Aquarius | -2.2 | 21.3" |
The coordinates above are given in J2000.0.
The sky on 24 Feb 2026
| The sky on 24 February 2026 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
62% 8 days old |
All times shown in PST.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source
The circumstances of this event were computed using the DE430 planetary ephemeris published by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
This event was automatically generated by searching the ephemeris for planetary alignments which are of interest to amateur astronomers, and the text above was generated based on an estimate of your location.
Related news
| 14 Jul 2050 | – Mars enters retrograde motion |
| 14 Aug 2050 | – Mars at opposition |
| 15 Aug 2050 | – Mars at perigee |
| 13 Sep 2050 | – Mars ends retrograde motion |
Image credit
© NASA/Hubble Space Telescope


