The Moon will pass in front of Saturn, creating a lunar occultation visible from south-western Alaska and Hawaii. Although the occultation will only be visible across part of the world – because the Moon is so close to the Earth that its position in the sky varies by as much as two degrees across the world – a close conjunction between the pair will be more widely visible.
The occultation will be visible from South El Monte. It will begin with the disappearance of Saturn behind the Moon at 07:11 PDT, though in daylight. Its reappearance will be visible at 08:07 PDT, though in daylight.
Extreme caution is necessary when pointing binoculars or telescopes at the sky when the Sun is above the horizon, as even a momentary glance at the Sun through such an instrument can cause permanent blindness.
The map below shows the visibility of the occultation across the world. Separate contours show where the disappearance of Saturn is visible (shown in red), and where its reappearance is visible (shown in blue). Solid contours show where each event is likely to be visible through binoculars at a reasonable altitude in the sky. Dotted contours indicate where each event occurs above the horizon, but may not be visible due to the sky being too bright or the Moon being very close to the horizon.
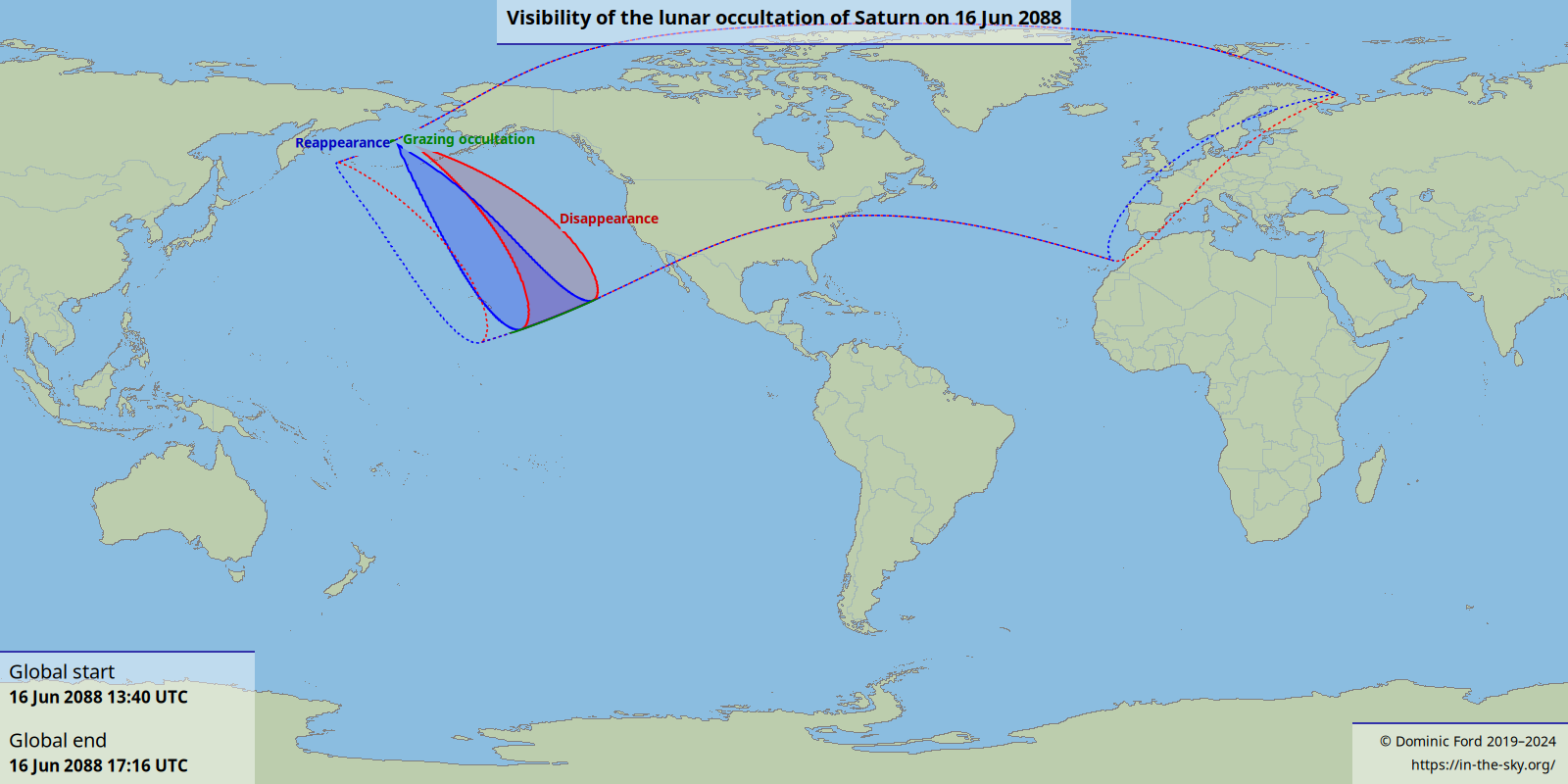
Outside the contours, the Moon will not pass in front of Saturn at any time, or is below the horizon at the time of the occultation. However, a close conjunction between the pair will be visible across much of the world.
The map can be downloaded in PNG , PDF or SVG format. A KMZ file , is also available, which can be opened in Google Earth to provide a higher resolution map.
The animation below shows the path of the occultation across the Earth's globe. The red circle shows where the Moon appears in front of Saturn.
A complete list of the countries and territories where the occultation will be visible is as follows:
| Country | Time span (UTC) |
| Alaska | 14:29–15:02 |
| Hawaii | 13:40–14:28 |
Lunar occultations are only ever visible from a small fraction of the Earth's surface. Since the Moon is much closer to the Earth than other celestial objects, its exact position in the sky differs depending on your exact location on Earth due to its large parallax. The position of the Moon as seen from two points on opposite sides of the Earth varies by up to two degrees, or four times the diameter of the full moon.
This means that if the Moon is aligned to pass in front of a particular object for an observer on one side of the Earth, it will appear up to two degrees away from that object on the other side of the Earth.
At the time of the occultation, the Moon will be 0 days past new moon and will be 9% illuminated. Saturn will disappear behind the illuminated side of the Moon and reappear from behind the unilluminated side of the Moon.
The position of Saturn at the moment of the occultation will be as follows:
| Object | Right Ascension | Declination | Constellation | Magnitude | Angular Size |
| Saturn | 03h15m20s | 15°54'N | Aries | 0.1 | 0'16" |
The coordinates above are given in J2000.0.
Next/previous occultations
| « Previous | Next » | |||
| Visible from the Contiguous United States | Worldwide | Worldwide | Visible from the Contiguous United States | |
| 24 Jul 2075 | 02 Jan 2082 | Occultations of Saturn | 14 Jul 2088 | 31 Oct 2088 |
| 31 May 2088 | 31 May 2088 | Occultations | 14 Jul 2088 | 17 Sep 2088 |
The sky on 1 Mar 2026
| The sky on 1 March 2026 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
98% 12 days old |
All times shown in PST.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source
The circumstances of this event were computed using the DE430 planetary ephemeris published by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
This event was automatically generated by searching the ephemeris for planetary alignments which are of interest to amateur astronomers, and the text above was generated based on an estimate of your location.
Related news
| 07 Jan 2088 | – Saturn ends retrograde motion |
| 07 Sep 2088 | – Saturn enters retrograde motion |
| 14 Nov 2088 | – Saturn at opposition |
| 20 Jan 2089 | – Saturn ends retrograde motion |
Image credit
The Moon in conjunction with Venus and Jupiter, with the Very Large Telescope in the foreground. Image © Y. Beletsky, ESO, 2009.


