Jupiter will reach opposition – the optimal time to observe it, when it will be visible for much of the night in the constellation Virgo. At this time, it also appears brightest in the sky and at its largest when viewed through a telescope.
From South El Monte, it will be visible between 19:58 and 05:36. It will become accessible at around 19:58, when it rises to an altitude of 7° above your eastern horizon. It will reach its highest point in the sky at 00:47, 44° above your southern horizon. It will become inaccessible at around 05:36 when it sinks below 7° above your western horizon.
A close approach to the Earth
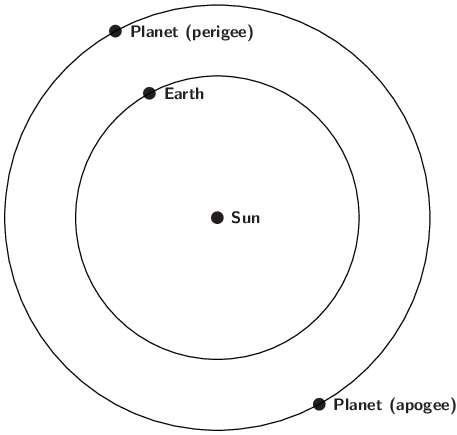
When a planet is at opposition, the solar system is aligned with that planet on the same side of the Sun as the Earth.
The term opposition refers to the moment when a planet passes opposite to the Sun in the sky. For those planets which orbit the Sun at a greater distance than the Earth – like Jupiter – this geometry occurs as the two planets pass each other in their orbits and they make closest approach – termed its perigee.
At opposition / perigee, planets are visible for much of the night, reaching their highest point in the sky around midnight local time, just as the Sun, 180° away, dips to its lowest point below the horizon.
Because it passes closest to the Earth at this time, the planet also appears at its brightest and largest around opposition.
The panels below show a comparison of the apparent size of Jupiter when seen at opposition in 2148, and when it is most distant from the Earth at solar conjunction.
In practice, the variation for Jupiter is quite modest since it orbits much further out in the solar system than the Earth – at an average distance from the Sun of 5.20 times that of the Earth. Consequently, its distance and angular size does not vary much as it cycles between opposition and solar conjunction. The variation is much greater for Mars, since it lies much closer to the Earth.
A comparison of the size of Jupiter as seen at 2148 opposition and at solar conjunction.
Observing Jupiter
At opposition, Jupiter is visible for much of the night. Even when it is at its closest point to the Earth, however, it is not possible to distinguish it as more than a star-like point of light with the naked eye, though a good pair of binoculars is sufficient to reveal it as a disk of light with accompanying system of moons.
A chart of the path of Jupiter across the sky in 2148 can be found here, and a chart of its rising and setting times here.
At the moment of opposition, Jupiter will lie at a distance of 4.43 AU, and its disk will measure 43.5 arcsec in diameter, shining at magnitude -2.5. At opposition, its celestial coordinates will be:
| Object | Right Ascension | Declination | Constellation | Magnitude | Angular Size |
| Jupiter | 14h06m30s | 11°15'S | Virgo | -2.5 | 43.5" |
The coordinates above are given in J2000.0.
Over the weeks following its opposition, Jupiter will reach its highest point in the sky around four minutes earlier each night, gradually receding from the pre-dawn morning sky while remaining visible in the evening sky for a few months.
The sky on 4 Mar 2026
| The sky on 4 March 2026 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
96% 15 days old |
All times shown in PST.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source
The circumstances of this event were computed using the DE430 planetary ephemeris published by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
This event was automatically generated by searching the ephemeris for planetary alignments which are of interest to amateur astronomers, and the text above was generated based on an estimate of your location.
Related news
| 24 Apr 2148 | – Jupiter at opposition |
| 26 Jun 2148 | – Jupiter ends retrograde motion |
| 26 Mar 2149 | – Jupiter enters retrograde motion |
| 26 May 2149 | – Jupiter at opposition |
Image credit
© NASA/Cassini


