The Moon will pass last quarter phase, rising in the middle of the night and appearing prominent in the pre-dawn sky.
From South El Monte, it will be visible from soon after it rises, at 23:32, until soon before it sets at 13:46.
At this time in its monthly cycle of phases, it appears almost exactly half illuminated.
The Moon orbits the Earth once every four weeks, causing its phases to cycle through new moon, first quarter, full moon, last quarter, and back to new moon once every 29.5 days.
As it progresses through this cycle, it is visible at different times of day. At last quarter, it rises in the middle of the night and appears high in the sky by dawn. It sets at around lunchtime. More information about the Moon's phases is available here.
Observing the Moon at last quarter
Over coming days, the Moon will rise later each day, so that it is visible for less time before sunrise and rises less far above the eastern horizon before dawn. By the time it reaches new moon, it will rise at around dawn and set at around dusk, making it visible only during the daytime.
Its daily progress is charted below, with all times are given in South El Monte local time.
| Date | Sun rises at |
Moon rises at |
Altitude of Moon at sunrise |
Direction of Moon at sunrise |
| 05 Sep 2020 | 06:26 | 20:56 | 35° | south-west |
| 06 Sep 2020 | 06:27 | 21:23 | 45° | south-west |
| 07 Sep 2020 | 06:27 | 21:51 | 55° | south-west |
| 08 Sep 2020 | 06:28 | 22:22 | 65° | south-west |
| 09 Sep 2020 | 06:29 | 22:56 | 74° | south-west |
| 10 Sep 2020 | 06:29 | 23:35 | 77° | south |
| 11 Sep 2020 | 06:30 | 00:20 | 71° | south-east |
| 12 Sep 2020 | 06:31 | 01:12 | 61° | east |
| 13 Sep 2020 | 06:32 | 02:11 | 50° | east |
| 14 Sep 2020 | 06:32 | 03:16 | 37° | east |
| 15 Sep 2020 | 06:33 | 04:25 | 24° | east |
| 16 Sep 2020 | 06:34 | 05:36 | 11° | east |
A thin crescent
The months around the autumn equinox – September and October in the northern hemisphere – present the best opportunity to see a very thin crescent Moon immediately before sunrise in the days running up to new moon.
This comes about because the Moon appears higher in the dawn sky sooner after new moon in the autumn months as compared to other times of year.
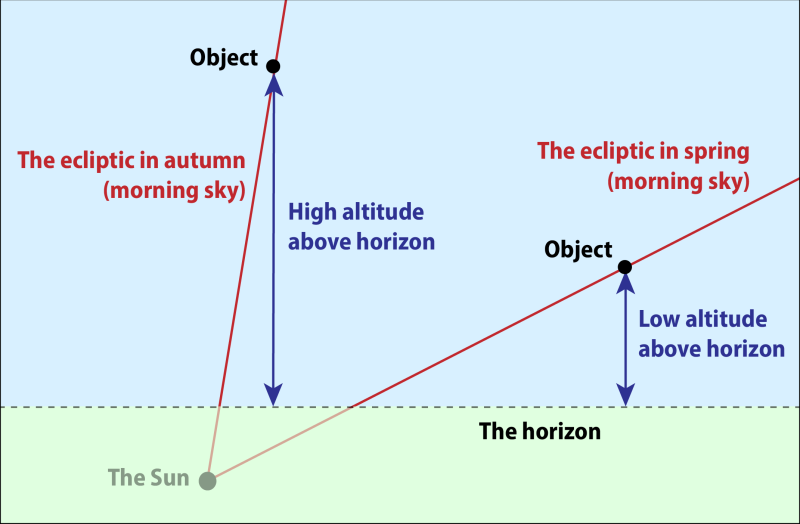
At all times, the Moon lies close to a line across the sky called the ecliptic, which is shown in yellow in the planetarium above. This line traces the path that the Sun takes through the zodiacal constellations every year, and shows the plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. Since all the planets circle the Sun in almost exactly the same plane, they too move across the sky following the same line.
When the Moon is widely separated from the Sun, it is separated from it along the line of the ecliptic. But, at different times of year, the ecliptic meets the horizon at different angles at sunrise. This means that a certain number of days after new moon, the Moon appears at different altitudes above the horizon at different times of year.
At sunrise, the ecliptic makes its steepest angle to the horizon at the autumn equinox – in September in the northern hemisphere, and in March in the southern hemisphere. Conversely, it meets the horizon at its shallowest angle at the spring equinox. And so, very thin crescent moons are most visible in the dawn sky in the autumn.
The inclination of the ecliptic plane to the horizon at South El Monte varies between 79° (sunrise at the autumn equinox) and 32° (sunrise at the spring equinox). On September 10, the ecliptic is inclined at 78° to the eastern dawn horizon.
The exact moment of last quarter
The exact moment of last quarter is defined as the time when the Moon's ecliptic longitude is exactly 90° away from the Sun's ecliptic longitude, as observed from the center of the Earth. However, the Moon does not appear in any way special at this instant in time, and a last quarter moon can be observed at any time in the pre-dawn sky.
At the moment it reaches last quarter, the Moon's distance from the Earth will be 396,000 km. Its celestial coordinates will be as follows:
| Object | Right Ascension | Declination | Constellation | Angular Size |
| The Moon | 05h07m20s | 22°15'N | Taurus | 30'08" |
The coordinates above are given in J2000.0.
The sky on 10 Sep 2020
| The sky on 10 September 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
43% 22 days old |
All times shown in PDT.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source
The circumstances of this event were computed using the DE430 planetary ephemeris published by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
This event was automatically generated by searching the ephemeris for planetary alignments which are of interest to amateur astronomers, and the text above was generated based on an estimate of your location.
Related news
| 10 Sep 2020 | – Moon at Last Quarter |
| 17 Sep 2020 | – New Moon |
| 23 Sep 2020 | – Moon at First Quarter |
| 01 Oct 2020 | – Full Moon |
Image credit
Simulated image courtesy of Tom Ruen.