Comet 2P/Encke will make its closest approach to the Sun on 2 July, at a distance of 0.34 AU.
From South El Monte on the day of perihelion it will not be readily observable since it will be very close to the Sun, at a separation of only 13° from it.
The events that comprise the 2020 apparition of 2P/Encke are as follows:
| Date | Event |
| 02 Jul 2020 | Comet 2P/Encke passes perihelion |
| 04 Aug 2020 | Comet 2P/Encke passes perigee |
The table below lists the times when 2P/Encke will be visible from South El Monte day-by-day through its apparition:
| Date | Constellation | Comet visibility |
| 11 Jun 2020 | Taurus | Not observable |
| 13 Jun 2020 | Taurus | Not observable |
| 15 Jun 2020 | Taurus | Not observable |
| 17 Jun 2020 | Taurus | Not observable |
| 19 Jun 2020 | Gemini | Not observable |
| 21 Jun 2020 | Gemini | Not observable |
| 23 Jun 2020 | Gemini | Not observable |
| 25 Jun 2020 | Gemini | Not observable |
| 27 Jun 2020 | Gemini | Not observable |
| 29 Jun 2020 | Gemini | Not observable |
| 01 Jul 2020 | Gemini | Not observable |
| 03 Jul 2020 | Gemini | Not observable |
| 05 Jul 2020 | Cancer | Not observable |
| 07 Jul 2020 | Cancer | Not observable |
| 09 Jul 2020 | Cancer | Not observable |
| 11 Jul 2020 | Cancer | Not observable |
| 13 Jul 2020 | Cancer | Not observable |
| 15 Jul 2020 | Leo | Not observable |
| 17 Jul 2020 | Leo | Not observable |
| 19 Jul 2020 | Sextans | Not observable |
| 21 Jul 2020 | Sextans | Not observable |
A more detailed table of 2P/Encke's position on each night is available here. A diagram of the orbit of 2P/Encke is available here.
Finder chart
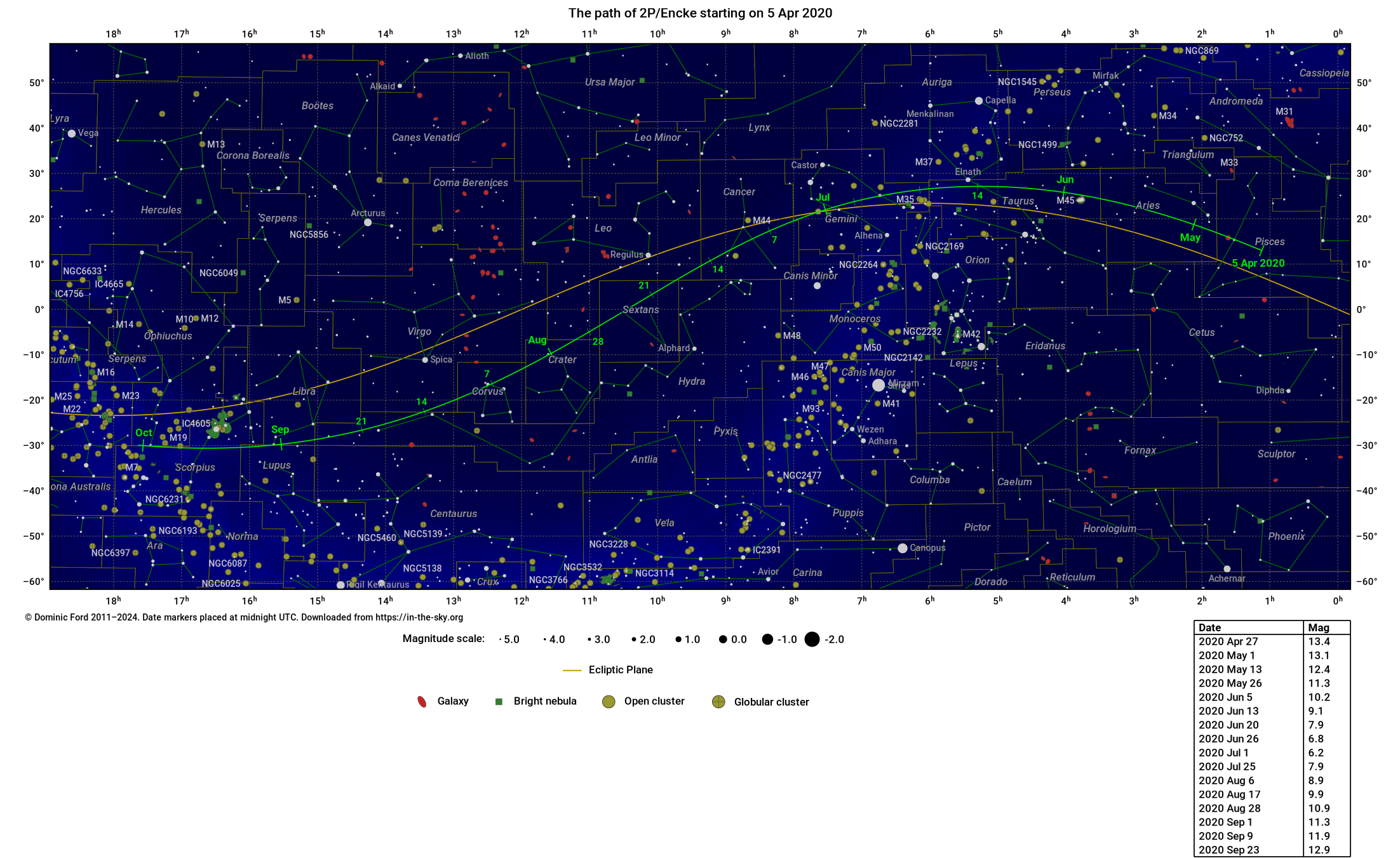
The chart below shows the path of 2P/Encke over the course of its apparition, as calculated from the orbital elements published by the Minor Planet Center (MPC). It is available for download, either on dark background, in PNG, PDF or SVG formats, or on a light background, in PNG, PDF or SVG formats. It was produced using StarCharter.
Comet brightnesses
Comets are intrinsically highly unpredictable objects, since their brightness depends on the scattering of sunlight from dust particles in the comet's coma and tail. This dust is continually streaming away from the comet's nucleus, and its density at any particular time is governed by the rate of sublimation of the ice in the comet's nucleus, as it is heated by the Sun's rays. It also depends on the amount of dust that is mixed in with that ice. This is very difficult to predict in advance, and can be highly variable even between successive apparitions of the same comet.
In consequence, while the future positions of comets are usually known with a high degree of confidence, their future brightnesses are not. For most comets, we do not publish any magnitude estimates at all. For the few comets where we do make estimates, we generally prefer the BAA's magnitude parameters to those published by the Minor Planet Center, since they are typically updated more often.
No estimate for the brightness of comet 2P/Encke is currently available.
The comet's position at perihelion will be:
| Object | Right Ascension | Declination | Constellation | Magnitude |
| Comet 2P/Encke | 07h45m10s | 20°54'N | Gemini | 6.2 |
The coordinates are given in J2000.0.
The sky on 2 Jul 2020
| The sky on 2 July 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
95% 11 days old |
All times shown in PDT.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warning
Never attempt to point a pair of binoculars or a telescope at an object close to the Sun. Doing so may result in immediate and permanent blindness.
Source
This event was automatically generated on the basis of orbital elements published by the Minor Planet Center (MPC) , and is updated whenever new elements become available. It was last updated on 23 Feb 2025.
Image credit
© Andy Roberts 1997. Pictured comet is C/1995 O1 Hale-Bopp.