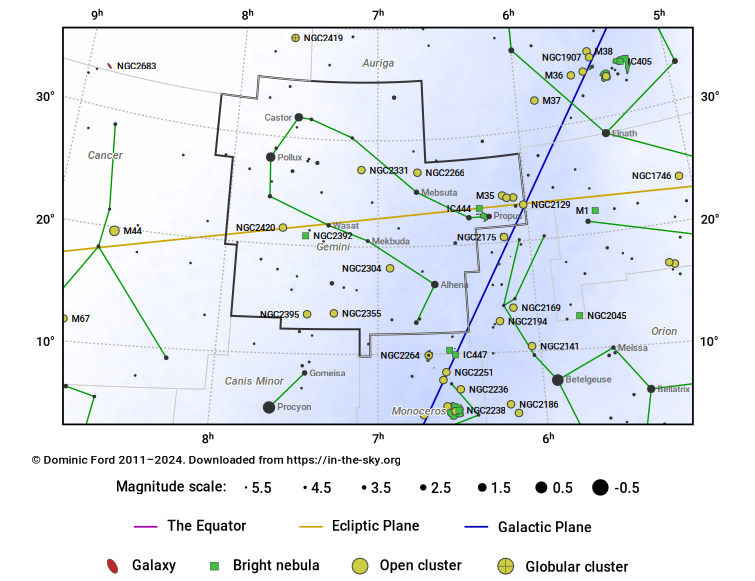
The Constellation Gemini
Gemini is a northern constellation, dominated by its two brightest stars, Castor and Pollux. It is visible throughout the northern winter months, culminating at midnight around New Year.
Both the galactic plane and the line of the ecliptic pass through this area of the sky: the Sun crosses the border from Taurus shortly after the June solstice, and remains in Gemini until late July.
Gemini is home to a number of open clusters, the brightest of which is M35.
The name ‘Gemini’ is Latin for twins, and refers to Castor and Pollux in classical mythology. Their mother was Leda, but they had different fathers. Castor was the son of Tyndareus, king of Sparta, while Pollux was the son of Zeus.
According to legend, Castor was killed in a family feud with his cousins, while Pollux was an immortal demigod. After his brother's death, Zeus offered Pollux the choice of sharing his immortality with his brother, and the two were forever cast into the sky.
Ancient
1.2% of the sky
513.8 square degrees
Hover the pointer over the name of an object to highlight its position on the starchart to the right, or click to see more information.
| Stars | Open Clusters | Globular Clusters | Galaxies |
| Pollux (mag 1.2) | Messier 35 (mag 5.1) | NGC 2339 (mag 11.8) | |
| Castor (mag 1.6) | NGC 2129 (mag 6.7) | NGC 2365 (mag 12.2) | |
| Alhena (mag 1.9) | NGC 2395 (mag 8.0) | NGC 2418 (mag 12.2) | |
| TYC1877-1716-2 (mag 2.3) | NGC 2420 (mag 8.3) | NGC 2481 (mag 12.5) | |
| α-Gem (mag 2.9) | IC 2157 (mag 8.4) | NGC 2487 (mag 12.6) | |
| μ-Gem (mag 2.9) | NGC 2331 (mag 8.5) | NGC 2342 (mag 12.6) | |
| Mebsuta (mag 3.0) | NGC 2158 (mag 8.6) | NGC 2492 (mag 12.7) | |
| Propus (mag 3.3) | NGC 2266 (mag 9.5) | NGC 2389 (mag 12.9) | |
| ξ-Gem (mag 3.3) | NGC 2355 (mag 9.7) | NGC 2290 (mag 13.0) | |
| Wasat (mag 3.5) | NGC 2304 (mag 10.0) | NGC 2289 (mag 13.2) | |
| λ-Gem (mag 3.6) | NGC 2234 | IC 486 (mag 13.2) | |
| κ-Gem (mag 3.6) | NGC 2265 | NGC 2291 (mag 13.2) | |
| θ-Gem (mag 3.6) | IC 2156 | NGC 2341 (mag 13.2) | |
| ι-Gem (mag 3.8) | NGC 2435 (mag 13.4) | ||
| Mekbuda (mag 4.0) | NGC 2486 (mag 13.5) | ||
| υ-Gem (mag 4.1) | NGC 2274 (mag 13.5) | ||
| ν-Gem (mag 4.1) | IC 2199 (mag 13.6) | ||
| ρ-Gem (mag 4.2) | NGC 2275 (mag 13.6) | ||
| 1-Gem (mag 4.2) | NGC 2379 (mag 13.6) | ||
| σ-Gem (mag 4.3) | NGC 2294 (mag 13.8) | ||
| τ-Gem (mag 4.4) | IC 2196 (mag 13.9) | ||
| 30-Gem (mag 4.5) | NGC 2333 (mag 14.1) | ||
| e-Gem (mag 4.7) | NGC 2449 (mag 14.1) | ||
| g-Gem (mag 4.9) | NGC 2370 (mag 14.2) | ||
| O-Gem (mag 4.9) | NGC 2498 (mag 14.3) | ||
| χ-Gem (mag 4.9) | NGC 2288 (mag 14.4) | ||
| φ-Gem (mag 5.0) | NGC 2411 (mag 14.4) | ||
| b-Gem (mag 5.0) | NGC 2357 (mag 14.5) | ||
| A-Gem (mag 5.0) | NGC 2454 (mag 14.5) | ||
| f-Gem (mag 5.0) | IC 454 (mag 14.5) |